Scaling-Up NCD Interventions in South East Asia
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are major cause of deaths globally and the burden of NCDs is rising disproportionately among lower income countries and populations. Three quarters of all NCDs deaths are in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC).
The increasing concerns on NCDs and their burden has led to a research project entitled “Scaling-Up NCD Interventions in South-East Asia (SUNI-SEA)” which is being delivered through a collaboration of ten consortium members from Europe and South-East Asia. This 4-year research project started in 2019 and is taking place in Indonesia, Myanmar and Vietnam.
The overall aim of the SUNI-SEA project is to evaluate and validate effective and cost-effective scaling-up strategies of evidence-based diabetes and hypertension prevention and management programmes, and apply results to enhance sustainable action for the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), based on experiences in South-East Asia.

Methodology
While countries in Europe struggle with ever-increasing costs of chronic diseases, Indonesia, Myanmar and Vietnam have developed innovative strategies to curb the epidemic of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes in an early phase, by
- moving NCD prevention and management from hospitals to primary healthcare facilities;
- involving communities and bringing prevention and self-management to the homes of people;
- linking NCD prevention to socio-economic development;
- introducing integrated financing of health prevention and clinical care for NCDs.
In short, these countries are trying to create innovative synergies within and between sectors. The stakeholders in South-East Asia expect that with a proper evidence base they will optimise their new initiatives in order to reach the full potential in reducing morbidity and mortality caused by NCDs.
SUNI-SEA will use the ongoing scaling-up activities on hypertension and diabetes prevention and management in Indonesia, Myanmar and Vietnam as starting point. It will link the existing activities, enhance the ongoing programmes, combine activities in communities and primary healthcare facilities, and monitor the scaling-up meticulously, in order to produce recommendations for scaling-up of NCD programmes.
Themes and research activities
The SUNI-SEA research project has three leading themes:
- Effectiveness of scaling-up hypertension and diabetes prevention and management interventions. How can countries increase access to prevention and care, by reaching more people who need care? How can countries remove barriers to prevention and care and make the service acceptable to people? And, how can countries improve the quality of prevention and care both at the community level and in primary health care facilities?
- Cost-effectivenessof scaling-up hypertension and diabetes prevention and management interventions. How can countries scale up the interventions and get the best value for money? Which financing mechanisms work better, now that lower-income countries are developing health insurance mechanisms to reduce catastrophic expenditure on NCDs? How can prevention best be financed in this context?
- Global NCD instruments, focusing on evidence-based methods in scaling-up NCD interventions and using them for sustainability and global innovative approaches in prevention and management, especially with regard to hypertension and diabetes
For the three leading themes effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and global NCD-instruments, comparative effectiveness research in combination with a participatory approach will be undertaken. Mixed methods will be used to gather qualitative and quantitative data.
Research sequence in SUNI-SEA
For all three themes, the same sequence of research activities will take place as shown in the figure below.
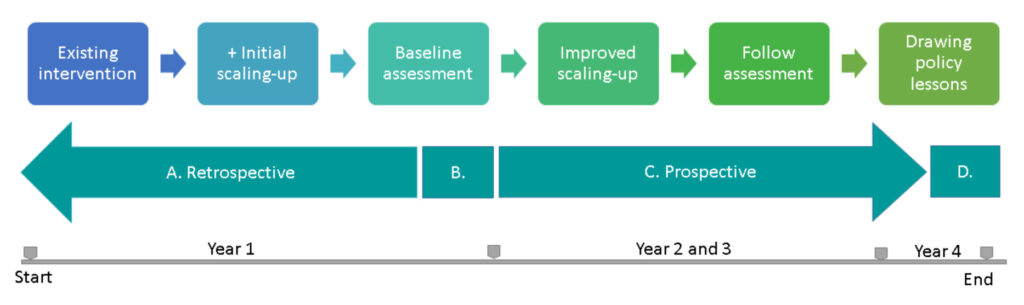
A. Retrospective study: In this phase, we will take stock of ongoing initiatives in communities and primary health care facilities to reduce the burden of diseases due to hypertension and diabetes in Indonesia, Myanmar and Vietnam. Which activities are best in reaching people, activating them to prevent NCDs and providing best screening and services? Which activities provide best value for money? This will consist of literature study, analysis of existing data from the countries and primary data collection to verify assumptions with regard to effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. The researchers will also make an assessment of quality of care provided.
B. Baseline assessment: The retrospective study will result in a baseline assessment of the existing activities, interventions, programmes and policies. Which are the most viable and likely to provide the optimum benefits for the countries? Which are likely to provide best results when scaled up?
C. Prospective study: In the prospective study researchers will engage in action research together with communities and primary health care facilities, focusing on the scaling up of the most viable interventions and programmes identified in the baseline assessment. In this phase it will be clear how best these interventions can be taken to a larger scale for replication countrywide and in other countries.
D. Findings and lessons for policy: In the last phase, SUNI-SEA will draw lessons learned for policy and create learning materials and instruments that can be used for improving global prevention and care in the case of non-communicable diseases.



